Models¶
Ella core module consist of four apps, two of them contain the main logic and
the second two provide basic CMS capabilities. The core logic is provided by
ella.core and ella.photos applications, see the image below for quick
overview of models used. Moreover, Ella ships with two basic CMS apps you can
use: articles and positions. Quick overview image follows.
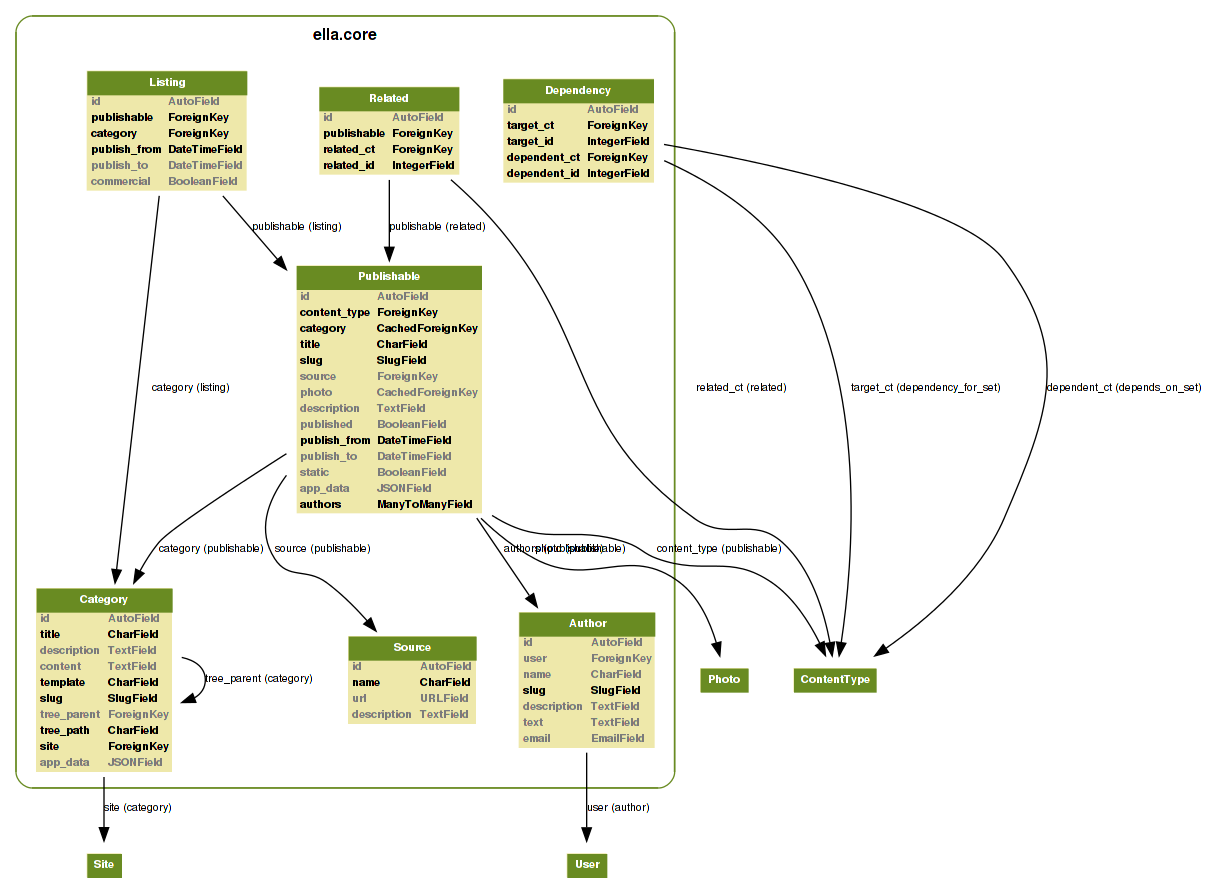
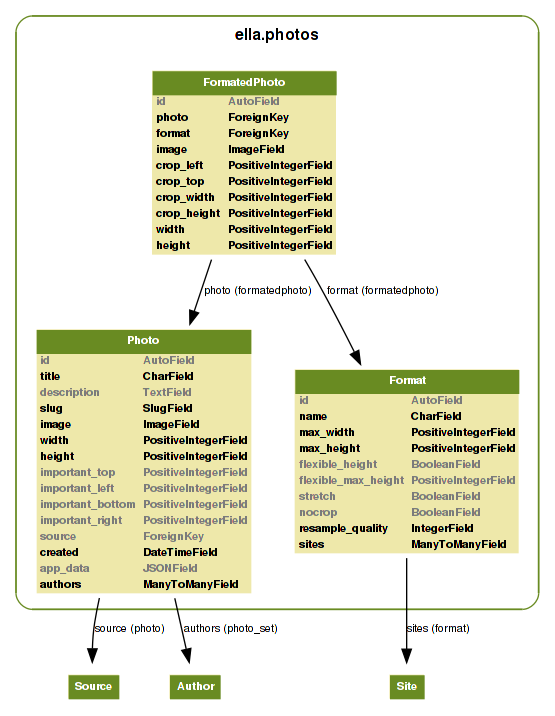
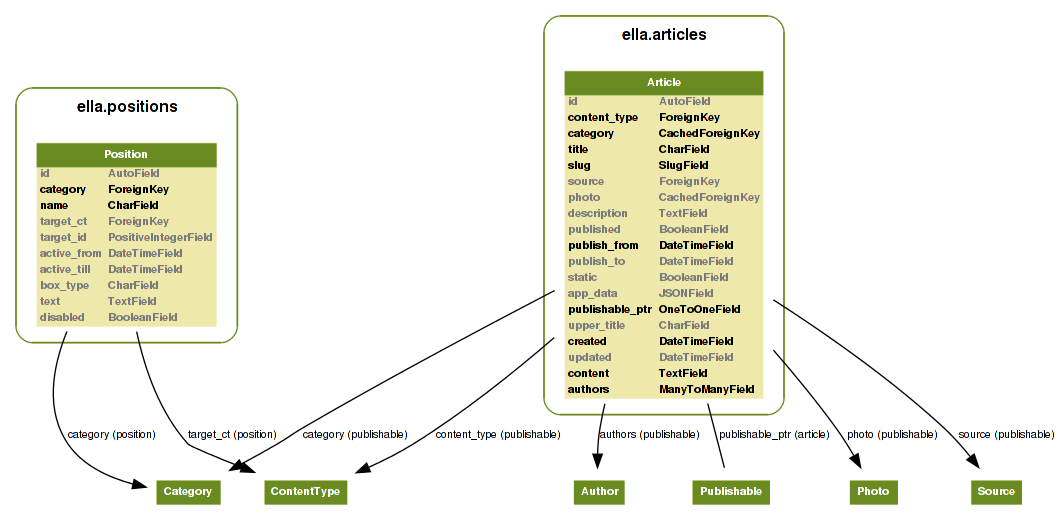
Core models¶
The Author model¶
-
class
ella.core.models.Author¶
Describes an Author of the published content. Author can be:
- Human
- Organization
- ...
All the fields except for slug are optional to enable maximum of
flexibility.
-
Author.user¶ Optional. Related Django
Userinstance. Can be blank and null.
-
Author.name¶ Optional. Name of the author.
-
Author.slug¶ Required. The only required field is slug. Must be unique.
-
Author.description¶ Optional. You may provide description of author.
-
Author.text¶ Optional. Small perex about the author. Use together with description to provide information about the author.
-
Author.email¶ Optional. When dealing with humans as authors, you can fill up his e-mail.
The Source model¶
-
class
ella.core.models.Source¶
A Source in oposition to Author is used for publishable content
that was taken from other sites and it’s purpose is mainly for legal matters.
-
Source.name¶ Required. The name of the source.
-
Source.url¶ Optional. If source is an organization, you may fill up their URL.
-
Source.description¶ Optional. Description about the source.
The Category model¶
-
class
ella.core.models.Category¶
Category is the basic building block of Ella-based sites. All the
published content is divided into categories - every Publishable object
has a ForeignKey to it’s primary Category. Primary category is then
used to build up object’s URL when using Category.get_absolute_url method.
Besides that, objects can be published in other categories (aka “secondary”
categories) via Listing.
Every site has exactly one root category (without a parent) that serve’s as the sites’s homepage.
Attributes¶
-
Category.title¶ Title of the category for common purposes.
-
Category.description¶ Optional. Description of the category for common purposes.
-
Category.content¶ When rendering static pages, this can come handy. It’s a rich-text powered field capable of holding HTML.
-
Category.template¶ Required. Template used for rendering the category. Defaults to
category.htmland can be overriden for custom layouts of the category detail.
-
Category.slug¶ Required. Slug for querying the category in URL.
-
Category.tree_parent¶ Relation to the parent category. When no parent category exists, the value is
Noneand such category is considered as root category. The prefered way of getting the parent isCategory.get_tree_parentmethod insted.
-
Category.main_parent¶ Returns parent category, which is considered as main. A main category is a category, whose parent is the root category.
-
Category.tree_path¶ Path in the category tree from the root. Is composed from the slug fields of the categories on the way joined by “/” symbol. It’s generated automatically.
Example:
"nested1/nested2"
-
Category.path¶ Returns tree path of the category. Tree path is string that describes the whole path from the category root to the position of this category.
-
Category.site¶ Required. A
Sitefromdjango.contrib.sitesframework, which category belongs to.
-
Category.app_data¶ Optional. A JSONField for keeping arbitrary data. See Extending category/publishable metadata for further information.
Methods¶
-
Category.get_tree_parent(self)¶ Returns tree parent or
Noneif not existent. Cached. Use in favor ofCategory.tree_parentattribute.
-
Category.get_absolute_url(self)¶ Returns absolute URL of the category. Useful in templates and views.
-
Category.draw_title(self)¶ Returns title indented by elements that can be used to show users a category tree.
Examples:
- no direct parent (the category root)
- TITLE
- one parent
- &nsbp;TITLE
- on third level of the tree
- TITLE
The Dependency model¶
-
class
ella.core.models.Dependency¶
-
Dependency.target_ct¶ ContentTypeof theDependency.target.
-
Dependency.target_id¶ Primary key of the
Dependency.target.
-
Dependency.target¶ Target of the dependency relation.
-
Dependency.dependent_ct¶ ContentTypeof theDependency.dependent
-
Dependency.dependent_id¶ Primary key of the
Dependency.target.
-
Dependency.dependent¶ Source of the dependency relation.
The Publishable model¶
-
class
ella.core.models.Publishable¶
Base class for all objects that can be published in Ella.
Attributes¶
-
Publishable.content_type¶ Automatically managed.
ContentTypeinstance of the Publishable subclass if applicable. Used to get the subclass instance in case a genericPublishableparent is dealt with which occurs for example when querying over all publishable objects.
-
Publishable.target¶ Automatically managed. Generic foreign key that points to the subclass instance for easy access. Cached to save the queries.
-
Publishable.category¶ Required. Main
Categoryobject aPublishableinstance belongs to. This has significant impact when building up the URL.
-
Publishable.title¶ Required. Verbose title of the publishable (gallery name, article title, ...).
-
Publishable.description¶ Optional. Basic description of the publishable. Can be used as perex, for instance.
-
Publishable.slug¶ Required. Slug to use when building up the URL. Needs to URL-friendly.
Required. A
ManyToManyrelation withAuthormodel to list publishable object’s authors.
-
Publishable.source¶ Optional. If the object comes from diferent source which needs to be listed, use this field.
-
Publishable.photo¶ Optional. The main photo of publishable objects. Main article photo for example.
-
Publishable.published¶ Required. A
BooleanFieldinstance keeping information if the object is already published or not. Works together withpublish_fromandpublish_tofields.
-
Publishable.publish_from¶ Required. Datetime keeping the start of publication period.
-
Publishable.publish_to¶ Required. Datetiem keeping the Finish of publication period.
-
Publishable.static¶ Required. A boolean whether the publication is static which means it’s not bound to some special date. Publication is valid forever.
-
Publishable.app_data¶ Optional. A container for arbitrary data on the model, for more info, see Extending category/publishable metadata.
Methods¶
-
Publishable.get_absolute_url(self, domain=False)¶ Returns absolute URL to the object without the domain and protocol.
Example:
"/news/2012/1/1/some-article-slug/"
-
Publishable.get_domain_url(self)¶ Returns full URL to the object with the domain and protocol added.
Example:
"http://www.example.com/news/2012/1/1/some-article-slug/"
-
Publishable.get_domain_url_admin_tag(self)¶ Domain url to be used in adminstration for showing the page link.
-
Publishable.is_published(self)¶ Returns
Trueif the Publishable is currently active,Falseotherwise.
The Listing model¶
-
class
ella.core.models.Listing¶
Listing of an Publishable in a Category. Each and every object that have it’s
own detail page must have a Listing object that is valid (not expired) and
places it in the object’s main category. Any object can be listed in any
number of categories (but only once per category). Even if the object is
listed in other categories besides its main category, its detail page’s url
still belongs to the main one.
Attributes¶
-
Listing.publishable¶ Required. A related
Publishableinstance to define the listing for.
-
Listing.category¶ Required. A
Categoryinstance where the listing should occur.
-
Listing.publish_from¶ Required. Datetime with start of the listing period.
-
Listing.publish_to¶ Required. Detaime with end of the listing period.
-
Listing.commercial¶ Optional. Set to
Trueif the listing is a commercial or ad related. These listings are usually marked with an ad warning. Defaults toFalse.
Methods¶
-
Listing.get_absolute_url(self, domain=False)¶ Returns absolute URL to the listing without domain and protocol parts.
Example:
"/news/2012/1/1/some-article-slug/"
-
Listing.get_domain_url(self)¶ Returns absolute URL to the list with the domain and protocol.
Example:
"http://www.example.com/news/2012/1/1/some-article-slug/"
Photo models¶
The Photo model¶
-
class
ella.photos.models.Photo¶
Represents original (unformated) photo uploaded by user. Used as source
object for all the formatting stuff and to keep the metadata common to
all related FormatedPhoto objects.
Attributes¶
-
Photo.title¶ Required. Human-readable title of the photo.
-
Photo.description¶ Optional description.
-
Photo.slug¶ Required. Slug to use when creating URL.
-
Photo.image¶ Required. Path to the uploaded image file.
-
Photo.width¶ Required. Original width of the uploaded image file.
-
Photo.height¶ Required. Original height of the uploaded image file.
important_* attributes describe the rectangular area on the photo, which
shouldn’t be cropped.
-
Photo.important_top¶
-
Photo.important_left¶
-
Photo.important_bottom¶
-
Photo.important_right¶
Required. A
ManyToManyrelation withAuthormodel.
-
Photo.source¶
-
Photo.created¶ Automatically managed. Keeps information when the photo was uploaded.
-
Photo.app_data¶ Optional. A container for arbitrary data on the model, for more info, see Extending category/publishable metadata.
Methods¶
-
Photo.__unicode__()¶ A human-readable representation of the
Photo.
-
Photo.get_absolute_url()¶ Full URL to the image file.
-
Photo.get_image_info()¶ Returns dictionary with keys
url,widthandheightholding metainformation about the image.Example:
>>> p = Photo.objects.get(pk=1) >>> p.get_image_info() >>> {'url': 'http://media.example.com/2011/1/23/img.jpg', 'width': 100, 'height': 200}
-
Photo.ratio()¶ Returns
floatholding the ratio between width and height ofNoneif not applicable.
-
Photo.get_formated_photo(self, format)¶ Returns
FormatedPhotoinstance for givenformat.
The Format model¶
-
class
ella.photos.models.Format¶
Defines per-site photo sizes together with rules how to adhere to them.
This includes:
- maximum width and height
- cropping settings
- stretch (rescale) settings
- sample quality
Attributes¶
-
Format.name¶
-
Format.max_width¶ Required. Integer with maximum width in pixels of the resulting image.
-
Format.max_height¶ Required. Integer with maximum height in pixels of the resulting image.
-
Format.flexible_height¶ Required. Boolean if height is “flexible”. If set to
True, the allowed height will be in rangemax_height-flexible_max_height.
-
Format.flexible_max_height¶ See
Format.flexible_heightabove.
-
Format.stretch¶ Required.
Trueif stretching can be used to ensure required dimensions. If set toFalse, only cropping will be used.
-
Format.nocrop¶ Required.
Trueif this format doesn’t do any cropping.
-
Format.resample_quality¶ Requried. Sampling quality to use when performing formating operations. Defaults to 85.
-
Format.sites¶ Django
Siteinstances that can use the format.
Methods¶
-
Format.get_blank_img(self)¶ Returns fake
FormatedPhotoobject to be used in templates when an error occurs in image generation. The result will be a dictionary with keysblank,width,heightandurlwhich points to storage while usingPHOTOS_EMPTY_IMAGE_SITE_PREFIXsetting.
-
Format.ratio(self)¶ Returns
floatholding the ratio between width and height.
The FormatedPhoto model¶
-
class
ella.photos.models.FormatedPhoto¶
Cache-like container of specific photo of specific format. Besides
the path to the generated image file, crop used is also stored together
with new width and height attributes.
Attributes¶
-
FormatedPhoto.photo¶ Related
Photoinstance that is being formated.
-
FormatedPhoto.format¶ Related
Formatinstance that is being used for formating.
-
FormatedPhoto.image¶ Source
Imageinstance.
The crop_* attributes keep information how the cropping was done if
peformed.
-
FormatedPhoto.crop_left¶
-
FormatedPhoto.crop_top¶
-
FormatedPhoto.crop_width¶
-
FormatedPhoto.crop_height¶
-
FormatedPhoto.url¶ Returns the URL of the resulting photo file.
The Article model¶
-
class
ella.articles.models.Article¶
Article is the most common publishable object. It can be used for
news on internet news pages, blog posts on smaller blogs or even for
news on an organization’s home page.
Attributes¶
-
Article.upper_title¶ Optional. Second title to use for special use cases.
-
Article.created¶ Automatically managed. Datetime when the article was created.
-
Article.updated¶ Set by user, optional. Datetime when the article was updated. This is not updated automatically and is in the control of users. Can be used for information to the readers when the article was last updated.
-
Article.content¶ Required. Rich-text field holding content of the article.
The Position model¶
-
class
ella.positions.models.Position¶
Represents a position – a placeholder – on a page belonging to a certain category.
Attributes¶
-
Position.name¶ A human-readable name for the position. This name is also used in templates when using the
{% position %}and{% ifposition %}templatetags.
-
Position.category¶ A
Categoryobject for which the position si defined. This is very important and used when resolving whichPositionobject to use for the place defined in template.
-
Position.target_ct¶ Optional. Django
ContentTypeinstance for the object to show in the position. Used together withtarget_idto find out the finaltarget.
-
Position.target_id¶
-
Position.target¶ Optional. Instance of the target object. In case nor
target_ctnortarget_idis set, raw HTML is rendered using thetextfield instead.
-
Position.text¶ Optional. When no specific object is bound to the position using the
targetattribute, raw HTML in this field is used.
-
Position.box_type¶ Optional. Box name to use when rendering
taget.
-
Position.active_from¶ Optional. Datetime holding information when to start showing this position. If kept to
None, no check is performed.
-
Position.active_till¶ Optional. Datetime holding information when to finish showing this position. If kept to
None, no check is performed.
-
Position.disabled¶ Optional. Defaults to
False. If set toTrue, position won’t be shown even though it is active.
Methods¶
-
Position.__unicode__(self)¶ Human-readable representation of the position.
-
Position.render(self, context, nodelist, box_type)¶ Returns the rendered position object. When position is bound to an object, box for the object will be rendered using
box_type. If no object is specified, raw HTML intextattribute use used as template.